
A SOP Template for Data Entry and Database Management provides a structured framework to ensure accuracy and consistency in handling data tasks. This template outlines step-by-step procedures for entering, verifying, and updating database records efficiently. It enhances data integrity while streamlining workforce training and operational workflows.
Data entry guidelines and data validation protocols.

This SOP defines data entry guidelines and data validation protocols to ensure accuracy, consistency, and integrity of data input processes. It includes standardized procedures for data collection, entry, verification, correction, and validation checks to minimize errors and maintain high quality data for reliable reporting and decision-making.
User access controls and authentication procedures.
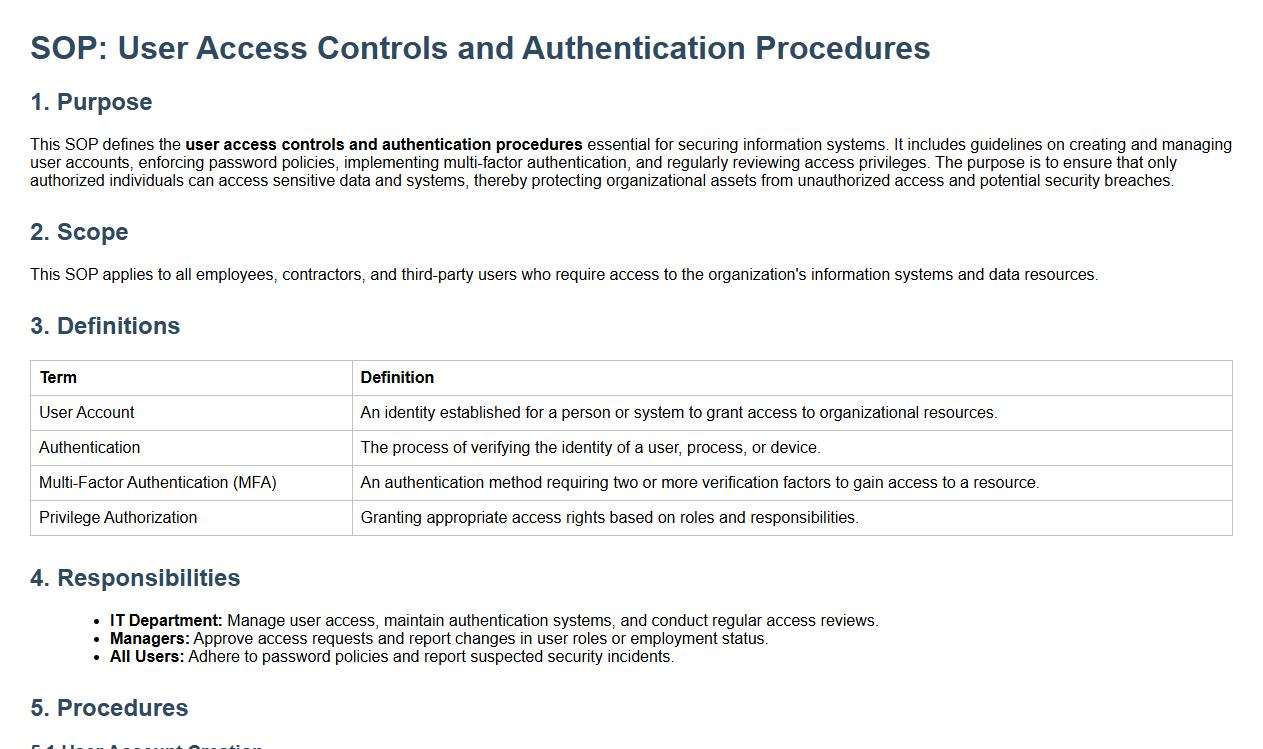
This SOP defines the user access controls and authentication procedures essential for securing information systems. It includes guidelines on creating and managing user accounts, enforcing password policies, implementing multi-factor authentication, and regularly reviewing access privileges. The purpose is to ensure that only authorized individuals can access sensitive data and systems, thereby protecting organizational assets from unauthorized access and potential security breaches.
Database backup and recovery processes.
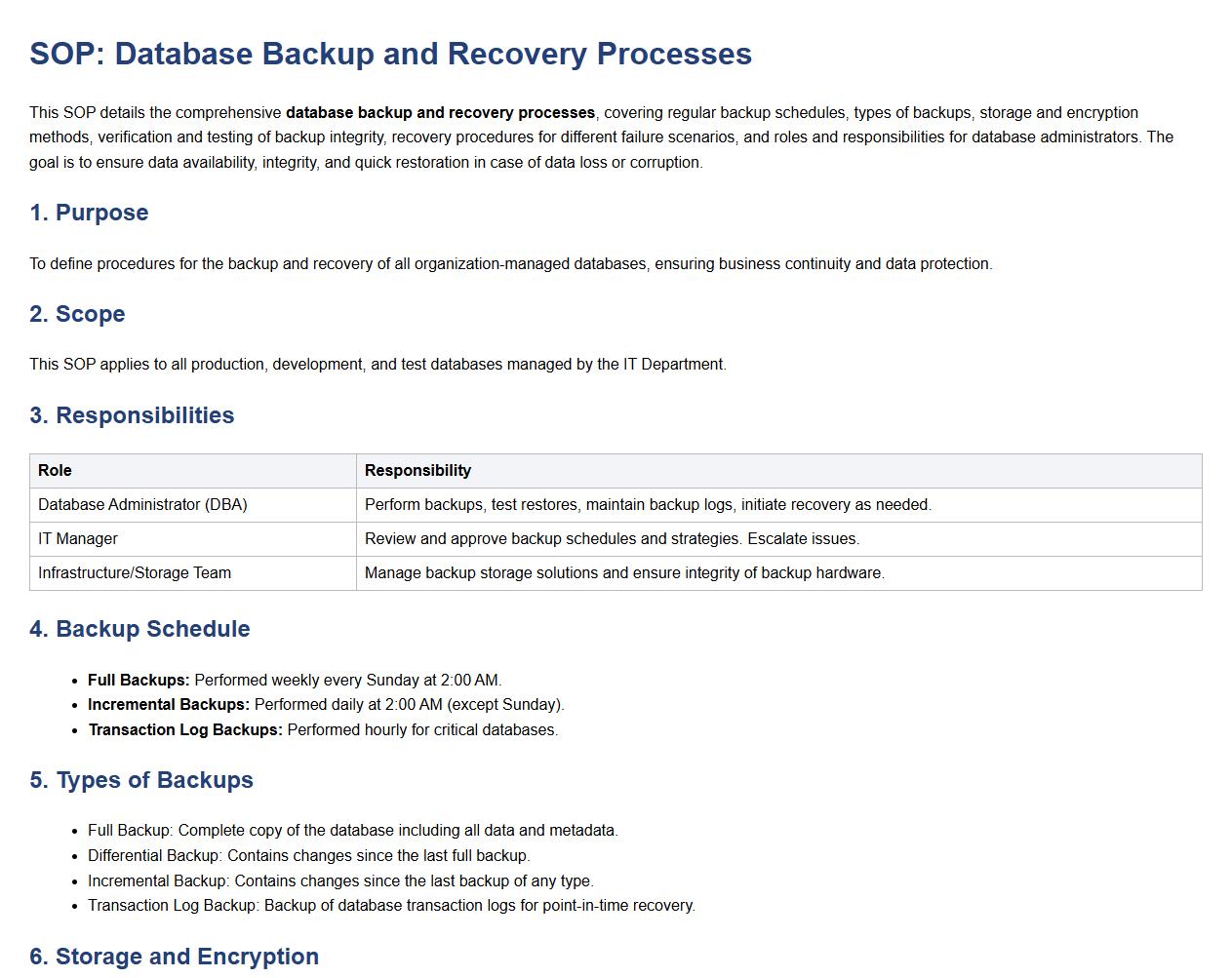
This SOP details the comprehensive database backup and recovery processes, covering regular backup schedules, types of backups, storage and encryption methods, verification and testing of backup integrity, recovery procedures for different failure scenarios, and roles and responsibilities for database administrators. The goal is to ensure data availability, integrity, and quick restoration in case of data loss or corruption.
Standard data formatting and naming conventions.

This SOP establishes standard data formatting and naming conventions to ensure consistency, accuracy, and clarity in data management processes. It covers guidelines for file naming, date and time formats, version control, metadata usage, and standardized data entry procedures. Adhering to these conventions facilitates efficient data retrieval, reduces errors, and supports effective collaboration across teams and systems.
Procedures for error identification and correction.

This SOP describes the procedures for error identification and correction, including methods for detecting errors, steps for analyzing root causes, guidelines for documenting issues, and protocols for implementing corrective actions. The goal is to ensure accuracy, maintain quality standards, and minimize the impact of errors on operations through timely and effective resolution processes.
Data import and export instructions.

This SOP provides detailed data import and export instructions, covering the processes for transferring data into and out of systems, ensuring data integrity and security, outlining steps for format compatibility, data validation, error handling, and documentation. It aims to facilitate efficient and accurate data exchange between various platforms and applications.
Routine database maintenance schedules.
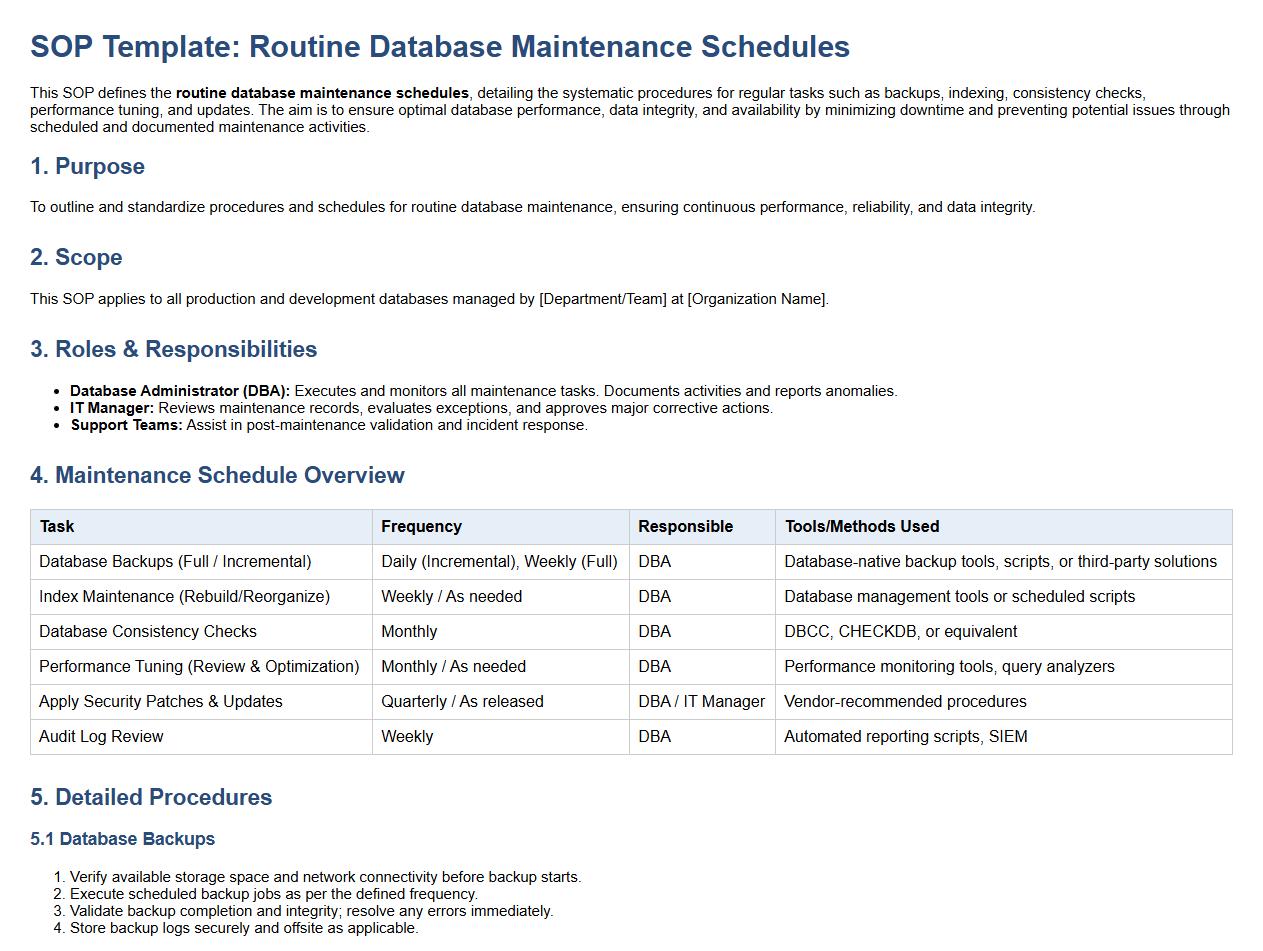
This SOP defines the routine database maintenance schedules, detailing the systematic procedures for regular tasks such as backups, indexing, consistency checks, performance tuning, and updates. The aim is to ensure optimal database performance, data integrity, and availability by minimizing downtime and preventing potential issues through scheduled and documented maintenance activities.
Data security and confidentiality measures.

This SOP details data security and confidentiality measures, covering data access controls, encryption protocols, secure data storage, user authentication processes, regular security audits, employee training on data privacy, incident response plans for data breaches, and compliance with relevant data protection laws. The objective is to safeguard sensitive information from unauthorized access, ensure data integrity, and maintain confidentiality across all organizational systems.
Audit trail and activity logging requirements.
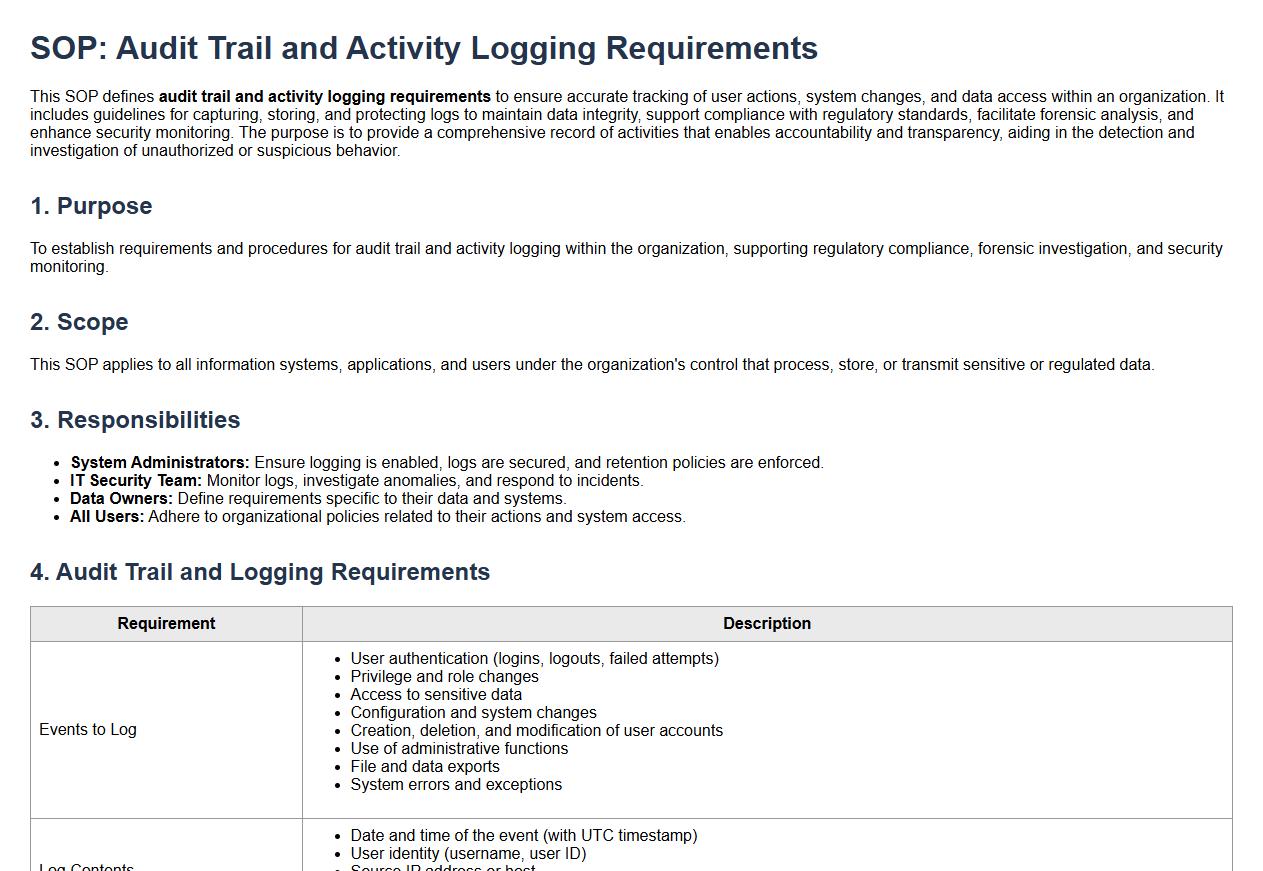
This SOP defines audit trail and activity logging requirements to ensure accurate tracking of user actions, system changes, and data access within an organization. It includes guidelines for capturing, storing, and protecting logs to maintain data integrity, support compliance with regulatory standards, facilitate forensic analysis, and enhance security monitoring. The purpose is to provide a comprehensive record of activities that enables accountability and transparency, aiding in the detection and investigation of unauthorized or suspicious behavior.
Periodic review and archiving of obsolete data.

This SOP establishes guidelines for the periodic review and archiving of obsolete data, including the identification, classification, and evaluation of data for relevance, secure archiving methods, data retention policies, access controls, and disposal procedures. The objective is to maintain data integrity, optimize storage resources, and comply with regulatory requirements by systematically managing outdated information.
Mandatory Data Validation Steps Before Database Entry
The SOP mandates rigorous data validation to ensure accuracy before entry into the database. It requires cross-referencing input data with original sources to eliminate errors. This process is crucial to maintain the reliability and quality of the database.
User Access Levels and Permissions for Database Management
The SOP clearly defines user access levels based on roles to protect sensitive information. Permissions are assigned to restrict or allow specific actions such as read, write, or admin rights. This systematic approach prevents unauthorized database modifications.
Data Backup Procedures for Ensuring Data Integrity
The SOP specifies regular data backup schedules to safeguard against data loss. Backups must be stored in secure, off-site locations and verified for completeness. These procedures are critical for disaster recovery and maintaining data integrity.
Approved Protocol for Correcting Data Entry Errors
According to the SOP, data entry errors must be corrected promptly with a documented audit trail. Corrections should be made by authorized personnel only, ensuring accountability. This protocol helps preserve the accuracy and traceability of the database.
Frequency of Database Audits and Responsible Parties
The SOP requires database audits to be conducted quarterly to ensure compliance and data quality. The responsibility for these audits lies with the designated Database Administrator or Compliance Officer. Regular audits help identify discrepancies and reinforce data governance.
